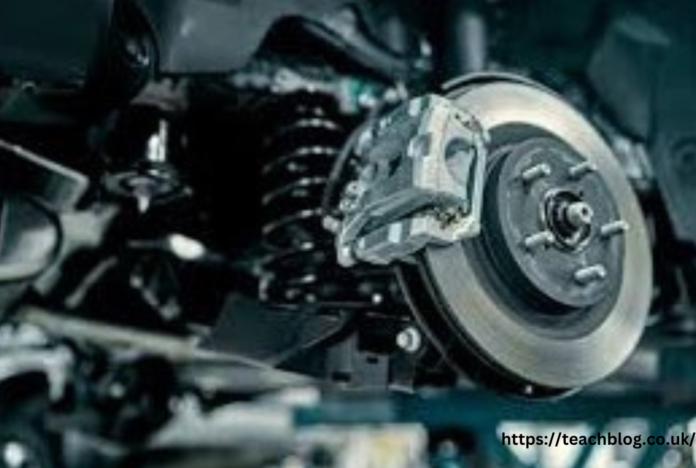
When it comes to vehicle safety, few components are as critical as the braking system. Among the various elements of this system, brake pads play a pivotal role in ensuring effective stopping power. Whether you’re upgrading your vehicle’s performance or simply replacing worn-out parts, choosing the right brake pads is essential. This comprehensive guide will help you understand the different types of brake pads, the materials they’re made from, and how to select the right ones for your car.
Table of Contents
Introduction
Brake pads are a vital part of your vehicle’s braking system, providing the friction needed to slow down or stop your car. Selecting the right brake pads isn’t just about picking a product off the shelf; it involves understanding your vehicle’s requirements, your driving style, and the differences between various brake pad materials. In this article, we’ll walk you through the process of choosing the right brake pads for your car, covering everything from the basics of how brake pads work to the different types available in the market.
What Type of Brake Pads Do I Need for My Car?
Selecting the correct brake pads begins with understanding your vehicle’s needs. The type of brake pads you require depends on several factors, including your car’s make and model, your driving habits, and the environment in which you typically drive. Here’s a breakdown of the main types of brake pads available:
1. Organic Brake Pads
Organic brake pads, also known as non-asbestos organic (NAO) pads, are made from a mixture of materials such as glass, rubber, and resins. These pads are known for their quiet operation and are typically softer, which makes them less harsh on brake rotors. Organic brake pads are a good choice for everyday driving in urban environments, where smooth, quiet braking is a priority. However, they tend to wear out faster and are not ideal for high-performance applications.
2. Semi-Metallic Brake Pads
Semi-metallic brake pads are composed of metal fibers mixed with organic materials. These pads offer a good balance between performance and durability. They provide excellent braking power and are more resistant to heat compared to organic pads, making them suitable for more aggressive driving styles and heavier vehicles. However, they can be noisier and may wear down brake rotors more quickly than other types.
3. Ceramic Brake Pads
Ceramic brake pads are made from ceramic fibers and nonferrous materials. They are known for their superior performance, durability, and low noise levels. Ceramic pads produce less dust compared to other types and are gentle on rotors, making them a popular choice for high-performance and luxury vehicles. However, they tend to be more expensive and may not perform as well under extreme conditions, such as high-speed racing.
4. Low-Metallic NAO Brake Pads
Low-metallic NAO brake pads are similar to organic right brake pads but include a small amount of metal, usually copper or steel, to improve performance. These pads provide better heat dissipation and braking power than organic pads but can be noisier and produce more dust. They are a good option for those looking for a balance between the quiet operation of organic pads and the performance of semi-metallic pads.
Brake Pad Materials and Their Advantages and Disadvantages
The material composition of right brake pads is crucial to their performance and longevity. Here’s a closer look at the advantages and disadvantages of the main brake pad materials:
1. Organic Brake Pads
- Advantages:
- Quiet operation
- Smooth braking feel
- Less wear on rotors
- Generally more affordable
- Disadvantages:
- Faster wear rate
- Less effective in high-heat situations
- Not suitable for heavy or high-performance vehicles
2. Semi-Metallic Brake Pads
- Advantages:
- Excellent braking power
- Better heat resistance
- Durable and long-lasting
- Suitable for a wide range of driving conditions
- Disadvantages:
- Noisier operation
- Can wear down rotors more quickly
- Produce more brake dust
3. Ceramic Brake Pads
- Advantages:
- Quiet and smooth operation
- Long-lasting with minimal wear
- Low dust production
- Gentle on rotors
- Disadvantages:
- Higher cost
- May not perform as well in extreme conditions
- Not always ideal for heavy-duty applications
4. Low-Metallic NAO Brake Pads
- Advantages:
- Improved braking performance over organic pads
- Better heat dissipation
- Balanced cost and performance
- Disadvantages:
- Noisier than organic right brake pads
- More brake dust production
- Can be harder on rotors
How Do Brake Pads Work?
Understanding how brake pads function is essential to appreciate their importance in your vehicle’s braking system. Brake pads are located within the brake calipers and press against the brake rotors (or discs) when you apply the brakes. This contact creates friction, which slows down the rotation of the wheels and, ultimately, brings the vehicle to a stop.
The braking process generates significant heat, especially during aggressive driving or in high-performance scenarios. The material of the right brake pads plays a critical role in managing this heat and maintaining effective braking performance. As brake pads wear down over time, they become thinner, reducing their ability to generate the necessary friction and heat dissipation. Regular inspection and timely replacement of brake pads are crucial to ensure safe and effective braking.
Brake Pad Friction Ratings
Brake pads are rated based on their friction coefficient, which measures the pad’s ability to generate friction against the rotor. The friction rating is typically represented by a two-letter code (e.g., “FF” or “GG”) found on the brake pad. The first letter represents the friction coefficient at low temperatures, while the second letter represents it at high temperatures. Here’s what these ratings mean:
- C to E: Low friction coefficient, typically found in economy-grade pads. These pads may not provide the best performance, especially under demanding conditions.
- F to G: Moderate friction coefficient, common in most OEM and aftermarket right brake pads. These offer a good balance of performance and longevity.
- H to Z: High friction coefficient, found in high-performance or racing Right Brake Pads. These pads provide excellent stopping power but may wear out faster and can be noisy.
Choosing the right friction rating depends on your driving style and needs. For everyday driving, a moderate friction rating (F or G) is usually sufficient. However, if you engage in high-performance driving or drive in conditions that demand frequent heavy braking, a higher friction rating may be necessary.
FAQs About Brake Pads
Q1: How often should I replace my brake pads?
A: Brake pad lifespan varies depending on the material, driving conditions, and driving style. On average, right brake pads should be replaced every 30,000 to 70,000 miles. Regular inspections are essential to determine when replacement is necessary.
Q2: Can I mix different types of brake pads on my vehicle?
A: It’s generally not recommended to mix different types of right brake pads on the same vehicle, as it can lead to uneven braking performance. It’s best to use the same type of brake pads on all wheels to ensure consistent braking.
Q3: Why are my brakes squeaking?
A: Brake squeaking can occur for several reasons, including worn-out pads, metal-on-metal contact, or the presence of dust and debris. If your brakes are squeaking, it’s important to have them inspected to determine the cause and prevent further damage.
Q4: What are the signs that my brake pads need to be replaced?
A: Common signs that your right brake pads need replacement include squeaking or grinding noises, longer stopping distances, a spongy brake pedal, and a warning light on the dashboard. If you notice any of these signs, it’s time to have your brakes checked.
Q5: Are ceramic brake pads worth the extra cost?
A: Ceramic right brake pads are often worth the investment if you prioritize quiet operation, low dust production, and long lifespan. They are ideal for everyday driving and high-performance vehicles. However, if cost is a concern, semi-metallic or organic pads may be more suitable.
Conclusion
Choosing the right brake pads for your car is crucial for ensuring safe and effective braking performance. By understanding the different types of brake pads, the materials they are made from, and how they work, you can make an informed decision that meets your driving needs and budget. Whether you opt for organic, semi-metallic, ceramic, or low-metallic NAO right brake pads, remember to consider your vehicle’s requirements and your driving habits to select the best option. Regular maintenance and timely replacement of right brake pads will keep your vehicle’s braking system in top condition, ensuring your safety on the road.